A Very Spanish Coup: What Can America Learn from the 1981 Spanish Coup
The storming of the American Capitol building on the 6th of January 2021 during a session to formalize Joe Biden’s presidential victory made headlines around the world. For many Americans, the fact that there was an armed attempt to disrupt a democratic transition of power was a worrying sign of democratic backsliding and the consequence of years of extreme partisanship. The siege suggested a grim vision of America’s political future. However, 40 years ago, the Spanish political system was able to recover from a similar event, in what could be an instructive experience for contemporary America. In February 1981, the Spanish political system, which had rapidly democratised following the death of General Francisco Franco in 1975, faced its first real …
Washington and Pyongyang: Back to Square One?
US administrations may change, but the North Korean problem, in all its guises, has plagued the United States for at least the past thirty years. The new Commander-in-Chief, Joe Biden, and his administration are facing increasing calls from the broader international community to clarify US policy towards East Asia, which includes China, Japan, and the two Koreas. The last Democratic administration, that of Barack Obama, focused on strengthening US bilateral alliances within the East Asian region, regional stability, and bolstering relationships with emerging powers. Yet, it did not fully address one of the greatest geopolitical challenges in the region: North Korea’s nuclear program. During the Obama administration, North Korea conducted four nuclear tests, one of which it claimed to be …
OxPol Blogcast Episode 4: Mexico’s Midterm Election
Welcome to the OxPol Blogcast, a podcast where we will be sharing research, analysis, and experiences from members of the University of Oxford’s Department of Politics and International Relations. On each, episode we will talk to a guest about a piece they’ve written for the OxPol Blog. Then, we’ll discuss their larger research agenda, their insights on conducting political science, and their time at Oxford. On this episode of the OxPol BlogCast, host Chase Harrison talks to DPhil student Javier Pérez Sandoval about Mexico’s upcoming midterm election, theories of voter choices, and analysing democracy at the subnational level. Read the original blog post here: https://blog.politics.ox.ac.uk/a-return-to-the-right-for-mexico-foucaults-pendulum-and-missed-political-opportunities/ Views expressed on this podcasts are those of the guests alone and are not representative of …
A Return to the Right for Mexico? Foucault’s Pendulum and Missed Political Opportunities
In June 2021, amidst the COVID-19 pandemic, Mexico will face what is bound to be one of the most complex mid-term elections the country has seen in the last two decades. At stake is control of 15 (out of 32) governorships, 30 state legislatures, 1,900 municipalities and a complete renewal of the Lower Chamber of Congress. The outcome will clearly be either a punishment or a reward for the leftist administration of Andrés Manuel López Obrador (AMLO) and the ballots cast this summer will undoubtedly make or break the second half of his presidency. The extent to which the COVID-shock has impacted individual political preferences in Mexico remains unclear. Looking at the most recent available data to conduct an exploratory …

Marijuana Legalization by Blunt Force: A Decade of US Policymaking through Ballot Initiatives
Election day 2020 was another big moment for drug policy reform in the US as voters across diverse states rejected the status quo and endorsed liberalizing drug laws. Arizona, Montana, New Jersey and South Dakota legalized marijuana for recreational purposes as the news proclaimed voters had “just said no to America’s war on drugs,” calling it “a banner year for drug decriminalization.” That election day brought significant wins for drug policy reform is not new. Beginning in 2012 with Colorado and Washington state, 13 out of the 15 states that have legalized recreational cannabis thus far have done so through ballot measures.[1] In 2014, Alaska and Oregon followed suit along with Nevada, Massachusetts, Maine and California in 2016 and Michigan …
Elections and the Politics of Fear in Uganda: The End of Post-Liberation Politics?
Zbigniew Brzezinski noted that the politics of fear is an efficient means of control because it “obscures reason and intensifies emotions.” After more than 34 years in power, President Museveni of Uganda—who toppled Milton Obote’s regime in 1986 after years in the bush with the National Resistance Movement (NRM)—understood the politics of fear better than anyone else. If one still had doubts, the death of around 40 people in Kampala at a political rally organized by Bobi Wine, Museveni’s main opponent, in November came to confirm one thing: it is election season in Uganda. On 14 January 2021, Ugandans will go to the polls. Museveni will most likely win re-election, after having scrapped the presidential term and age limits in 2005 and 2017 respectively. However, this piece argues that the intense politics of fear used by his regime can be interpreted as the possible end of post-liberation politics in Uganda. Post-liberation …
The Crown’s Irresponsible Adviser, the Governor General, and the Australian Constitutional Crisis of 1975: A Smoking Gun?
On 14 July, following legal proceedings, the National Archives of Australia released correspondence between Sir John Kerr, who served as Governor General of Australia from 1974–77, and Sir Martin Charteris, the Principal Private Secretary (PPS) to the queen. The letters concern Kerr’s decision to dismiss Gough Whitlam, the Labor Prime Minister, who was then locked in a battle between the House of Representatives, where he held a majority, and the Senate, which opposed him and was blocking supply (the federal budget). Leading scholars, such as Anne Twomey, as well as Buckingham Palace, have argued that the letters contain no smoking gun connecting Kerr’s actions to the monarch or her PPS. However, we believe that we can see a wisp of smoke. And it lingered. Kerr and Charteris …
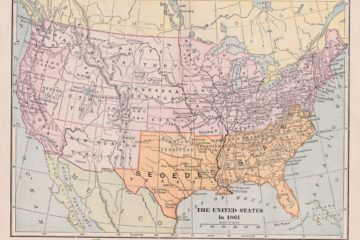
Comparing the 1860 and 2020 Elections: Is the USA Heading for Another Civil War?
All summer, as protests raged over the United States, fears grew that an increasingly polarised United States was heading for another civil war. There was great worry over violence erupting across the land, and a distinct sense that there were at least two rival and distinct Americas in the country: Red America and Blue America. Political movements such as the Lincoln Project and the Wide Awake Boys explicitly made comparisons between the present time and the Civil War-era. Almost two thirds of Americans, in May 2020, believed that the country was close to civil war. The 2020 presidential election might therefore have the same effect as that of 1860 election: then, the election of Abraham Lincoln as President persuaded the …









