
The 2015 EU “Refugee Crisis” : Analysing the IOM’s Information Campaign in Senegal
In 2015, Europe witnessed a significant increase in the influx of migrants, commonly referred to as the “2015 EU refugee crisis.” This article explores how this “crisis” transformed the migration-development agendas. With a specific focus on IOM’s information campaign in Senegal, I argue that the EU’s post-crisis migration policy has been characterised by the securitisation and externalisation of borders, reinforcing a pre-existing development agenda that primarily serves the political interests of EU states. What makes Senegal’s information campaign noteworthy is its use of affective, emotional, and relatable content to discourage Senegalese people from embarking on “irregular” journeys, rather than resorting to explicit violence such as highly militarised border controls. Although 2015 may sound like a long time ago, this type …

Small States shaping EU Policies: Latvia and the Disinformation Threat
In the aftermath of Ukraine’s Euromaidan Revolution of 2013-14, pro-Kremlin propaganda reached unprecedented levels. It started spreading confusion and distrust in Western institutions more easily and rapidly than ever before. Latvia, a small nation formerly part of the Soviet Union and home to a significant ethnic Russian minority, perceived an acute threat to European stability and convinced the entire European Union (EU) to take action. This article explores how Latvia managed to influence EU policy-making, providing valuable lessons on small state influence in the EU and important insights into the origins and framing of counter-disinformation policies in Europe. Background In 2015, Latvia persuaded other EU member states to create the East StratCom Task Force, an influential unit within the European …

Assessing the Performance of Minority Governments in Europe: The Devil is in the Detail
In 1974, when Harold Wilson formed the UK’s first minority government in 45 years, observers like Anthony King optimistically claimed that “[m]inority rule can work”. This challenges the oft-cited view of Strøm that minority governments are “counterintuitive phenomen[a] in the world of parliamentary democracy”. Today, minority governments constitute approximately one third of governments in established parliamentary democracies, globally. This ‘counterintuitive’ statistic raises the following questions: When can minority rule work? Under which conditions are minority cabinets effective? How have minority rule governments evolved over time? To answer these questions, I focus on three cases – Sweden, Norway, and Denmark – where minority cabinets are the predominant form of government. Ultimately, I argue that existing measures to assess the performance of …

OxPol Blogcast. Politics, Re-Imagined — Democratic Backsliding with Vicente Valentim
As we witness a rise in radical right politics in Europe and beyond, our host Cassandra van Douveren speaks to Dr. Vicente Valentim, a Postdoctoral Prize Research Fellow at Nuffield College at the University of Oxford. Vicente’s work focusses on the role of social norms in normalising the expression of views and behaviours associated with authoritarianism. Join us as we discuss his upcoming book, The Normalisation of the Radical Right: A Norms Theory of Political Supply and Demand (forthcoming: September 2024), pathways to restore democratic norms and Vicente’s hopes for the future. Politics, Re-Imagined is a series by the Department of Politics and International Relations (DPIR) at the University of Oxford focused on exploring tangible and sustainable solutions to the …

King in his own chess game: Orbán, the Hungarian “special path” and international ambitions
It was a matter of “religious freedom” – following a request from Serbia, Hungary’s veto on the sanctioning of Patriarch Kirill would have been expected. It was one of the interesting takeaways from of a few days spent in the company of pro-Fidesz politicians, pastors, and public intellectuals at the Tusványos summer festival. Gathered in the heart of Romania – home to a sizeable minority of ethnic Hungarians, about 6 per cent of the population – it struck me that Orbán’s story is not just a story of Hungary. It is a story of the region, of Europe, and of Hungary’s place in the world. A new story about Hungary When Orbán came to power for the second time in …

Wandel durch Handel: Germany’s strategic diplomacy vis-à-vis China and Taiwan
Relations between Germany and Taiwan strengthened in 2022, despite Germany’s reluctant acceptance of Beijing’s One China Policy. Meanwhile, bilateral economic ties with both Taiwan and China have sparked discussions about Germany’s foreign policy goals and whether Berlin is reviving the antiquated diplomatic strategy known as Wandel durch Handel (“Change through Trade”) amidst Europe’s growing security vulnerabilities. In June 2023, Germany and the Chinese state-owned firm COSCO signed a contract for the sale of shares in Hamburg’s seaports. Chancellor Olaf Scholz’s visits to Taiwan, once unimaginable , were strategically timed to coincide with the contract. Two months later, Germany established an agreement with TSMC, Taiwan’s largest semiconductor company. Prevailing narratives among policy circles view Wandel durch Handel as a relic from Germany’s regulatory …
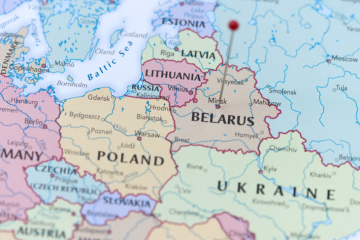
Wrong Analytical Lenses Undermine the West’s Belarus Policy
Belarus, a country of 9.2 million people in Eastern Europe, is portrayed in Western media and diplomatic circles in a simplistic and unnuanced way: in addition to its decades-long description as Europe’s last dictatorship, it is now also perceived as a Russian satellite state, springboard for hybrid threats, including illegal migration, to the EU, and a co-aggressor in Moscow’s war on Ukraine. Such perceptions particularly dominate the discourses and shape the policies towards Belarus of its immediate neighbours among EU and NATO member states – Poland, Lithuania, and Latvia. Indeed, tensions on Belarus’s borders with these states have risen sharply in recent years. Since 2020, Warsaw, Vilnius, and Riga have spearheaded the introduction of harsh Western sanctions and border closures, …

Russia’s War in Ukraine and Women’s Agency
Despite the unabated destruction and devastation caused by Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine, the war also opened new doors for development and a leap in women’s agency. Ukraine is fundamentally rethinking gender roles, expanding the opportunities of its citizens, and serving as a model for other countries. The Armed Forces of Ukraine have become the first place where women’s voices have been amplified. Ukraine has allowed women to participate in military operations to guarantee national security and defence, as they repel and deter armed aggression by Russia. Currently, 40,000 women serve in the Armed Forces, including those in combat roles. Furthermore, 8,000 women hold officer positions, and 5,000 serve on the front lines. In the near future, a separate combat …







