
Breaking the Domino Effect: How the West Should Respond to Niger’s Coup
On 26 July, Niger’s presidential guard launched a coup against President Mohamed Bazoum, announcing their seizure of power in a televised broadcast. As the dust of the coup begins to settle, Niger — and the international community — stand at a crossroads. The military junta’s success in maintaining power is far from guaranteed and has been widely condemned. Several states and supranational organisations, including the US, France, the EU, the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), and the African Union (AU) have threatened the military junta with sanctions if it does not reinstate President Bazoum, and have even considered military intervention. However, the Sahel’s track record of successful coups suggests that Niger is likely to see further democratic backsliding, …

As IS territorial dominance diminishes, what challenges lie ahead for Iraq’s Kurds?
On the ninth of June, Haider al-Abadi, the Iraqi Prime Minister, arrived in Mosul to congratulate the armed forces for the liberation of the city. Mosul had been conquered by the so-called Islamic State in Iraq and Syria (ISIS) in 2014 and served as its Iraqi capital. This significant victory is not yet the end of ISIS in Iraq, however, both in Iraq and in Syria its territorial dominance has strongly diminished—by about 60 % since January 2015—and is likely to continue. The power vacuum emerging from this rapid decline has heated up competition between the numerous parties in the conflict—regular forces of regional states and great powers, as well as various militias often acting as their proxies—to control former …
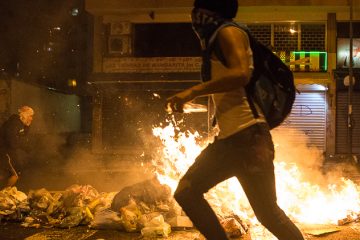
Venezuela’s instability has far broader implications. Here’s what’s at stake
Venezuela seems locked in a downward political and economic spiral. But what happens in Venezuela has far broader implications for international security. “Here you must not speak badly about Chávez” — this was the message on banners at a Colombia-Venezuela border bridge I crossed recently on a research trip. It was just one of the signs of the exponential jump in authoritarianism in Venezuela, and the continued unravelling of the regime. Last Saturday, Chief Prosecutor Luisa Ortega, a critic of the government of President Nicolás Maduro, was dismissed. On Sunday, a military uprising left one dead and several injured, then other military dissidents used social media to call for other soldiers to disobey the president. By Tuesday, parliament was practically …

Irrelephant: The Misleading Connections Between Terrorism and Ivory Poaching
The world is experiencing an ‘environmental crime crisis’. Dwarfed only by the trafficking of drugs, humans and counterfeit goods, the illegal wildlife trade is estimated to be the fourth largest type of transnational organised crime. But compared to the smuggling of bullets and bodies, wildlife crime is vastly under-researched. Most people have not even heard of the world’s most trafficked mammal, the humble and far from headline-grabbing pangolin. Yet one area of this booming illicit trade receives more attention than most: poaching for ivory and rhino horn. Driven by growing Asian prosperity, particularly in Vietnam and China, a revived market for ivory and horn has expanded to unprecedented heights for modern times. Accompanying this growth is a narrative which connects …

Why has “ISIS” so far Failed in India?
The so-called Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS)/Daesh is a relatively new terror organisation, but one with large and gruesome ambitions. Their activity in the Middle East, European capitals and American suburbs gain most of the headlines, but areas of Asia and Africa are hardly immune. On paper, India looks vulnerable. It is part of the imagined Khorasan territory of the ancient caliphate that ISIS seeks to recreate. It has the third largest Muslim population in the world, the majority of them Sunni. Some fear this population is a fertile recruitment ground for radicalization. Though ISIS vows to wipe out the Shia Muslim and Hindu populations in the country, to date no attack has taken place within India. The …

New Challenges – Is the Taliban in Transition?
On 21st May, an American airstrike killed Taliban leader Mullah Akhtar Mansour in the Pakistani province of Baluchistan. This operation, which involved multiple drones, comes as a relief to many, as Mansour had been actively planning and carrying out attacks across Afghanistan. According to the US Secretary of State John Kerry, Mansour ‘posed a continuing imminent threat to US personnel in Afghanistan, Afghan civilians, Afghan security forces, and members of the US and the NATO coalition.’ The killing of the Taliban leader, however, is likely to lead to unwelcome consequences, and will hamper peace talks between the insurgents and the government. The issue of peace talks has always been unpopular among the Taliban’s most senior leadership. In the wake of Mansour’s …

Coup attempt and terror bombings demonstrate Turkish lives don’t matter to Erdoğan and the AKP
Last week’s coup attempt by military forces in Turkey — the military’s first overt attempt to take power since 1980 — came as a great shock to the international community. At least 290 people were killed and 1,440 wounded. The coup also spurred a dramatic wave of purges; less than 24 hours after the turmoil began, 2,839 army members and a member of the constitutional court were arrested, while 2,745 judges and five members of the Supreme Board of Judges and Prosecutors were removed from their posts. The purges only intensified thereafter; within a week, about 60,000 soldiers, police, judges, civil servants and teachers found themselves detained, suspended or under investigation. The government’s rhetoric and consistent inaction, contextualized within its wider response to the …

‘Charlie Hebdo’ and the end of the French exception
Today many are asking why Parisians have been attacked in their own city, and by their own people. But for many years the question for those following the issues of foreign policy and religion was why France had suffered so little terrorism in comparison to other European states. After the bombs on the Paris Metro and a TGV line in 1995, there were no significant Islamist attacks until the fire-bombing of the Charlie Hebdo office in November 2011, and the killings of three French soldiers (all of North African origin) and three Jewish children (and one teacher) by Mohamed Merah in Toulouse four months later. These attacks turn out to have been a warning of things to come.
But why was France free of such attacks for over fifteen years, when Madrid and London suffered endless plots and some major atrocities? Given the restrictions placed by successive governments on the foulard (headscarf) and the burka, together with the large French Muslim population (around 10% of the 64 million total), the country would seem to have been fertile ground for fundamentalist anger and terrorist outrages.
One view is that the French authorities were tougher and more effective than, say, the British who allowed Algerian extremists fleeing France after 1995 to find shelter in the Finsbury Park Mosque — to the fury of French officials. Another line is that the French secular model of integration, with no recognition of minorities or enthusiasm for multiculturalism, did actually work. Thus when riots took place in 2005 the alienated youth of the banlieues demanded jobs, fairness, and decent housing — not respect for Islam or Palestinian rights.
A third possible explanation of the long lull before this week’s storm is that French foreign policy had not provoked the kind of anger felt in Spain and Britain by their countries’ roles in the Iraq war, which France, Germany, and some other European states had clearly opposed. Although France had an important role in the allied operations in Afghanistan, its profile was not especially high. Given the slow-changing nature of international reputations the image of France as a friend of Arab states and of the Palestinians endured, while Britain drew hostile attention as the leading ally of the United States in the ‘war against terror’. France, again unlike Britain and the United States, has tended to be pragmatic in negotiations with those who have taken its citizens hostage abroad, facilitating the payment of ransoms and getting them home safely. Its policy was that payments, and the risk of encouraging further captures, were preferable to providing the Islamists with global publicity.









