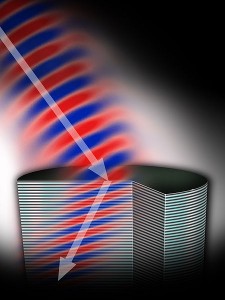
Cloaks of Invisibility: The latest frontier in military technology
Fiction and reality have meshed to incredible extents in the past decades, and it is no longer a surprise to see sci-fi-inspired inventions used in everyday life. The military field has been no exception and is now at the cusp of groundbreaking innovations that could change war-making to its core.
The next frontier in defense technology is so-called “stealth” technologies, in which the U.S. military has already invested huge funds. New research is opening up the prospect of achieving something close to invisibility on the battlefield, a breakthrough likened to Harry Potter`s famous invisibility cloak. While most stealth technologies are designated to elude enemy radars, new invisibility technologies could conceal objects in real time, not just from radar but from the naked eye.
The science of invisibility took off in the mid 2000s. This research has mostly involved the use of metamaterials, which are extremely thin composites that bend electromagnetic waves in a way that negatively refracts lights. Cloaking mechanisms use metamaterials to route light waves around an object and create the sensation of looking through the object.

The Neurochemistry of Power: Implications for Political Change
Power, especially absolute and unchecked power, is intoxicating. Its effects occur at the cellular and neurochemical level. They are manifested behaviourallynin a variety of ways, ranging from heightened cognitive functions to lack of inhibition, poor judgment, extreme narcissism, perverted behaviour, and gruesome cruelty.
The primary neurochemical involved in the reward of power that is known today is dopamine, the same chemical transmitter responsible for producing a sense of pleasure. Power activates the very same reward circuitry in the brain and creates an addictive ‘high’ in much the same way as drug addiction. Like addicts, most people in positions of power will seek to maintain the high they get from power, sometimes at all costs. When withheld, power – like any highly addictive agent – produces cravings at the cellular level that generate strong behavioural opposition to giving it up. In accountable societies, checks and balances exist to avoid the inevitable consequences of power. Yet, in cases where leaders possess absolute and unchecked power, changes in leadership and transitions to more consensus-based rule are unlikely to be smooth. Gradual withdrawal of absolute power is the only way to ensure that someone will be able to accept relinquishing it.

What is the future for the ‘China governance model’?
The leadership turnover in China last year took place in a shifting political situation. Namely, there have been increased calls for more political accountability and multi-candidate elections, broader media freedom and financial reform.
We need to watch this closely. How China’s leadership reacts to these calls for change will determine whether it will continue its phenomenal ‘rise’ or be hampered by intransigence.
Let’s take a closer look at the context. The uprisings in the Arab world have prompted many to ask whether China will be the next to be swept along in a wave of popular unrest that has toppled rulers in several countries. Indeed, the Chinese leadership, both in power and previously in power, has been watching the situation carefully. This attention has been particularly justified considering that the current Chinese president assumed power at a time when social media became a real force. These new forms of communication played an undisputable role in the Arab and Maghreb uprisings. Now, half a billion Chinese are registered on Sina Weibo, a website much like Twitter. This online platform has served “netizens” to voice many complaints ranging from governance malfunctions and corruption to food and environmental issues.
This raises inevitable questions. Is the bid for democratic reform a matter of time? Might the prediction of an “end of history” and of a uniform move in the direction of liberal democracy make a comeback? Or, might there be other sustainable alternatives?

Moving away from the end of history to a sustainable history
Two decades ago, the ‘End of History’, à la Francis Fukuyama, seemed a plausible prediction for many in the West. At least, it was a prophecy many hoped would turn into a self-fulfilling prophecy. In the climate of reinvigorated faith in the virtues of liberal democracy post-1989, freedom and democracy were two common buzzwords that indeed seem to carry a strong promise for the future. They also seemed indissolubly linked and interchangeable.
Western-type liberal democracy in its current form remains the most tested and successful accountable governance model in history. However, as a slogan for global political change in the 21st century, it needs to be re-examined both in terms of its applicability to all forms of societies and for making current democratic societies more inclusive. The range of events now in the spotlight of international relations – such as the Arab Spring – has further emphasized that the bid for leadership change, be it highly authoritarian, might in fact be premised on a quest for something more wholesome than just political freedom.










