
OxPol Blogcast. Politics, Re-Imagined — Displacement and the World Economy with Alexander Betts
How can we ensure that displaced people live in safety and dignity and create a policy that is sustainable at the same time? In this episode, we speak to Dr. Alexander Betts, the Leopold Muller Professor of Forced Migration and International Affairs at the Refugee Studies Centre, and the Director of the Refugee Economies Programme, both at the University of Oxford. Alexander has written extensively on the political economy of refugee protection — highlighting how displaced people can access and contribute to economies worldwide. Politics, Re-Imagined is a series by the Department of Politics and International Relations (DPIR) at the University of Oxford focused on exploring tangible and sustainable solutions to the most pressing challenges facing humanity today. Listen on:

Review of Alt-Finance: How the City of London Bought Democracy by Marlène Benquet and Théo Bourgeron (Pluto Press, 2022)
For years academic literature and broader public debates have largely framed the Brexit referendum as a ‘popular revolt against the elites’. While some emphasised the role of economic factors and others boiled it down to anti-immigration attitudes, most accounts seem to converge around this bottom-up perspective that ordinary people disillusioned with the elites have driven the UK out of the EU. Conversely, apart from a few dissenting voices, the idea that economic elites have been mostly opposed to Brexit has been the prevailing view in the literature. Challenging the over-emphasis on the voting process, Marlène Benquet (University of Paris Dauphine) and Théo Bourgeron (University of Edinburgh) invite us to look more closely at the role played by the economic interests …

China’s Role in Restructuring Debt in Africa
Africa’s public debt burden has doubled from 2010 to date. Data from the International Debt Statistics Data as of December 2022 shows that African countries owe $ 644855.2 billion (USD). The International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank consider 22 low-income African countries to be either in debt distress or at high risk of debt distress as of November 2022. Debt distress in this context means a country is experiencing difficulties in servicing its debt. A high debt burden could risk the continent’s economic growth, development, and climate investments. The additional global economic downturn and falling commodity process could compound the issue for countries on the continent. While there is no immediate threat of systemic and financial collapse due …

A New Direction for US Democracy Promotion?
As a prominent global aid donor, democracy promotion has distinctively shaped U.S. foreign assistance activities. Democracy aid has been a prominent theme of U.S. foreign assistance since the Marshall Plan. More recently, between 2001 and 2015, the U.S. annually disbursed $18 billion on average in democracy and governance aid, which represents (on average) 43% of the total U.S. foreign aid budget (calculated by the author from U.S. Government data and including Department of Defence figures). Nevertheless, the relationship between institutions and aid is complex and disputed. Scholars argue that inclusive and equitable institutions underpin economic growth and catalyse foreign assistance. Yet aid may also feed back on institutions, strengthening, weakening, or consolidating them. In December 2021, President Biden reflected on …
Within the EU, Redistributive CAP Mechanisms Can Make a Big Difference for Small Farms
The proverbial thunderclouds are finally dispersing over the fields and farms of Europe. The protracted negotiations over the European Union’s next Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) budget, which began in 2018, finally concluded in June with a provisional agreement between the EU’s Commission, Council, and Parliament. While the storm is not officially over – Parliament must ratify the deal in the coming autumn – the warring factions have retreated to lick their wounds for the time being, with both environmentalists and small farmers frustrated that the final proposals either did not address their demands or did so in a watered-down fashion. Of particular concern to small farmers’ groups is the mandatory implementation of policies designed to redistribute CAP funds and level …
Colombian Mass Protests: Foretelling an Emerging Latin American Debt Crisis?
S&P, a global credit rating agency, recently downgraded Colombia’s credit rating to a non-investment grade, implying that Colombian government bonds are now high-risk financial assets. The downgrade hit the country amid a wave of mass unrest. For over a month, Colombians spanning all strata of society protested in large numbers. Sparked initially by opposition to a government-proposed tax reform, which President Ivan Duque soon retracted, protesters expressed diverse demands, including calling for the Duque administration to resign, a series of social and economic reforms, a thorough implementation of Colombia’s 2016 peace agreement, and an end to police brutality. Protesters thus have called for nothing less than a complete overhaul of Colombia’s political and economic system. The protests form part of …
OxPol Blogcast Episode 5: Biden’s North Korea Policy
Welcome to the OxPol Blogcast, a podcast where we will be sharing research, analysis, and experiences from members of the University of Oxford’s Department of Politics and International Relations. On each, episode we will talk to a guest about a piece they’ve written for the OxPol Blog. Then, we’ll discuss their larger research agenda, their insights on conducting political science, and their time at Oxford. On this episode of the OxPol BlogCast, host Chase Harrison talks to Stipendiary Lecturer in Politics Edward Howell about Biden’s policy on North Korea, regional relations around the Korean Peninsula, and exact you conducts research on a notoriously closed off country like North Korea. Read the original blog post here: https://blog.politics.ox.ac.uk/washington-and-pyongyang-back-to-square-one/
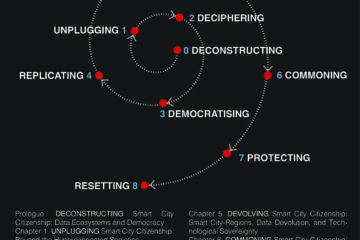
Smart City Citizenship: A Techno-Political Review (of Cities and Nations)
COVID-19 has hit European citizens dramatically, not only creating a general risk-driven environment with a wide array of economic vulnerabilities but also exposing them to pervasive digital risks, such as biosurveillance, misinformation, and e-democracy algorithmic threats. Over the course of the pandemic, a debate has emerged about the appropriate techno-political response when governments use disease surveillance technologies to tackle the spread of COVID-19. Citizens have pointed out the dichotomy between state-Leviathan cybercontrol and civil liberties. Moreover, the giant technological flagship firms of surveillance capitalism, such as Google, Amazon, and Facebook, have already assumed many functions previously associated with the nation-state, from cartography to the disease surveillance of citizens. But particularly, amidst the AI-driven algorithmic disruption and surveillance capitalism, Smart City Citizenship sheds light on the way citizens …








