OxPol Blogcast Episode 7: Latin America’s Emerging Debt Crisis
Welcome to the OxPol Blogcast, a podcast where we will be sharing research, analysis, and experiences from members of the University of Oxford’s Department of Politics and International Relations. On each, episode we will talk to a guest about a piece they’ve written for the OxPol Blog. Then, we’ll discuss their larger research agenda, their insights on conducting political science, and their time at Oxford. On this episode of the OxPol BlogCast, host Chase Harrison talks to DPhil student Christoph Sponsel about Colombia’s credit rating, the Latin American debt crisis of the 1980s, and doing work at the intersection of political science and economics. Read the original blog post here: https://blog.politics.ox.ac.uk/colombian-mass-protests-foretelling-an-emerging-latin-american-debt-crisis/
How Can Political Theory Be More Useful to Policymaking?
Recently, scholars have reflected on how to make political theory more relevant to policy. While most of the ideas around this charge are centered around the debate between ideal and non-ideal theories¹, one might ask whether there are other methodological insights we can advance to make political philosophy more useful to politics and society. In this piece, I suggest that one avenue that should be explored consists of building a bridge between political theory and comparative political economy to theorise varieties of ideal regimes. As vaccination campaigns proceed throughout the globe, policymakers, activists, and scholars are thinking about what the post-Covid world will look like and how to repair their national economy. Many view this moment as a critical juncture …
Why Police Reform Won’t Do the Trick in Colombia
Times are grim for human rights and the rule of law in Colombia. Since the end of April, tens of thousands of Colombians have taken to the streets after President Iván Duque announced a controversial tax reform. While the government has withdrawn the reform proposal, protests are ongoing as citizens express their frustration over structural inequalities. Discontent is high across the country, especially among lower- and middle-class Colombians who have experienced increased hardship while enduring the COVID-19 pandemic. By 22 June, 83 people were killed and over 1,600 wounded, with much of the violence attributed to the Colombian National Police. The police’s anti-riot unit, known as ESMAD, has become a symbol of disproportionate policing based on the excessive use of force. The Constitution …
Impacts of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Water-Energy-Food Nexus
In a recently published journal article, we argue that there is a pressing need for a systemisation of the impacts of COVID-19 on water, energy and food security. We also explore the tangible impacts of the pandemic, including negative aspects, like increase in medical waste, and positive aspects, like some improvements in air quality and carbon emissions. The COVID-19 pandemic offers an opportunity to examine the impacts of system-wide crises on key supply sectors, such as water, energy, and food. These sectors are becoming increasingly interlinked in environmental policy-making and with regard to achieving supply security. Now, there is a pressing need for a systematization of impacts and responses beyond the disruptions on individual supply sectors. Specifically, this paper provides …
OxPol Blogcast Episode 4: Mexico’s Midterm Election
Welcome to the OxPol Blogcast, a podcast where we will be sharing research, analysis, and experiences from members of the University of Oxford’s Department of Politics and International Relations. On each, episode we will talk to a guest about a piece they’ve written for the OxPol Blog. Then, we’ll discuss their larger research agenda, their insights on conducting political science, and their time at Oxford. On this episode of the OxPol BlogCast, host Chase Harrison talks to DPhil student Javier Pérez Sandoval about Mexico’s upcoming midterm election, theories of voter choices, and analysing democracy at the subnational level. Read the original blog post here: https://blog.politics.ox.ac.uk/a-return-to-the-right-for-mexico-foucaults-pendulum-and-missed-political-opportunities/ Views expressed on this podcasts are those of the guests alone and are not representative of …
A Return to the Right for Mexico? Foucault’s Pendulum and Missed Political Opportunities
In June 2021, amidst the COVID-19 pandemic, Mexico will face what is bound to be one of the most complex mid-term elections the country has seen in the last two decades. At stake is control of 15 (out of 32) governorships, 30 state legislatures, 1,900 municipalities and a complete renewal of the Lower Chamber of Congress. The outcome will clearly be either a punishment or a reward for the leftist administration of Andrés Manuel López Obrador (AMLO) and the ballots cast this summer will undoubtedly make or break the second half of his presidency. The extent to which the COVID-shock has impacted individual political preferences in Mexico remains unclear. Looking at the most recent available data to conduct an exploratory …
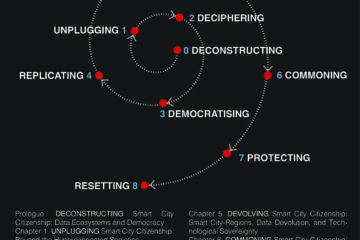
Smart City Citizenship: A Techno-Political Review (of Cities and Nations)
COVID-19 has hit European citizens dramatically, not only creating a general risk-driven environment with a wide array of economic vulnerabilities but also exposing them to pervasive digital risks, such as biosurveillance, misinformation, and e-democracy algorithmic threats. Over the course of the pandemic, a debate has emerged about the appropriate techno-political response when governments use disease surveillance technologies to tackle the spread of COVID-19. Citizens have pointed out the dichotomy between state-Leviathan cybercontrol and civil liberties. Moreover, the giant technological flagship firms of surveillance capitalism, such as Google, Amazon, and Facebook, have already assumed many functions previously associated with the nation-state, from cartography to the disease surveillance of citizens. But particularly, amidst the AI-driven algorithmic disruption and surveillance capitalism, Smart City Citizenship sheds light on the way citizens …
Covid-19 and Prison Populations: the case for priority vaccine allocation
As we enter 2021 and the Covid-19 pandemic rumbles on, optimism for the coming year relies heavily on successful vaccine rollout. Attention is now increasingly focussed on the practicalities of distribution, which will involve prioritisation and difficult policy decisions. Few argue about those groups right at the top of the list like care home residents, or healthcare staff working in high risk settings. However, an important population is less on the radar: people in prison. There are around 11 million people in prison around the world. Most will be in environments that make social distancing and other measures to reduce transmission, now a routine part of day-to-day community life for most, much more challenging. Such conditions can make prisons vulnerable …









