
General election 2017: votes from anywhere
Some six months before Theresa May called a surprise general election, The Road to Somewhere was published. In it, David Goodhart argues that the old political divide, between left-wingers and right-wingers, has been superseded. The electorate, Goodhart claims, is now better divided between “anywheres” and “somewheres”. Peter Wiggins looks at the Goodhart argument in the context of the 2017 general election. Of “Anywheres”, “Somewheres” and “Inbetweeners” According to The Road to Somewhere, roughly 25% of the population are “anywheres” – they are mobile, metropolitan, liberal, tolerant, at home wherever they may be, and wary of group attachment. These voters are likely to be highly educated, and they tend to approve of “mass immigration,” subscribing, as Goodhart puts it, to “progressive …

The young(-ish) have spoken. What now?
When Teresa May announced her snap election last April, she not only ruined my Roman holiday, but also made me cringe about having written a blog in the immediate aftermath of the Brexit referendum in which I had encouraged just that, namely: “Go with Dignity – Call a Snap Election!” Why? By then I had accepted the prevailing wisdom that the Conservatives would win a landslide victory, providing them with a three-figure majority in the Commons. This would have given her the popular mandate to push through Brexit in the ‘hardest’ possible form, thus nullifying any chance for a second ‘in-out’ referendum on the outcome of the Article 50 negotiations, which I had by then advocated in “The Will of …
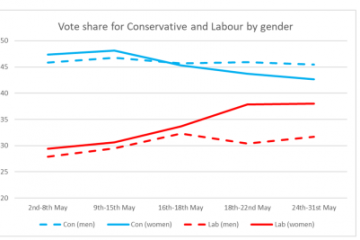
Labour Poll Surge Thanks To Not Just Younger, But Also Older Women
Coverage of recent polls has suggested that women are becoming more supportive of Labour and that this is driving the recent tightening of the election race. The figure below shows the average vote intention separately for men and women on average using data from a range of different pollsters (see methodological note below). At the beginning of May there was very little gender gap. The Conservative lead was much the same for men as for women. For polls conducted in the past week, on average the Conservatives still had a large, 14-point lead amongst men, but only a small, 4-point lead amongst women. Compared with the start of May, women are now 7 points more likely to vote Labour than …
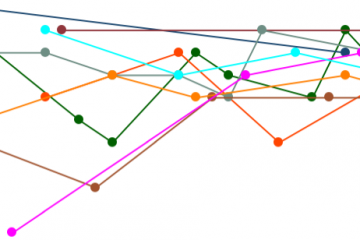
The UK General Election 2017: What’s been happening in the polls?
Since the general election was called Labour have gone up in the GB vote intention polls while the Liberal Democrats and especially UKIP have dropped. The Conservatives have fluctuated but on average remained steady. The following graph shows the overall trends. Looking at those pollsters that have published at least two polls since 18th April, the picture is pretty consistent for Labour, the Liberal Democrats and UKIP. As following three graphs of GB polls by fieldwork end date show, the trends are pretty much the same for nearly all pollsters. The more complicated picture is for the Conservatives. They went up on average at the beginning of the campaign, but, as the graph below shows, this was true for some …

Another Labour Meltdown?
The polls in Scotland just before the last election showed a 21-point lead for SNP over Labour. The SNP went on to take all but one of Labour’s 41 Scottish seats. This week Theresa May called a general election in the wake of polls showing her Conservative party 21 points ahead of Labour. Could Labour now be headed for a Britain wide meltdown of the kind that they suffered in Scotland two years ago? Intriguingly, the distribution of the 2015 Labour share of the vote across the seats they are defending now is very similar to the distribution of their 2010 share of the vote in the Scottish seats that they were defending in 2015. In both sets the vast …

Prime Minister Theresa May’s Early Election Call and the Fixed-term Parliaments Act
Theresa May has this morning announced that she intends to call a general election on June 8 in a bid to increase the size of her parliamentary majority and to reduce the ability of opposition parties to extract concessions from the government during Brexit negotiations. This raises the question of how she plans to achieve the election, given that the Fixed-term Parliaments Act (2011) removed the Prime Minister’s ability to trigger general elections. Under the Act, an early election can only be called under two conditions; (i) if the government is defeated in a vote of no confidence and parliament does not vote to express confidence in a government within two weeks, or (ii) if a two-thirds parliamentary majority endorses …









