Russia’s constitutional reform and Putin’s plans for a legacy of stability
On 15 January, President Vladimir Putin called for a “greater balance between the branches of power” as he announced significant changes to the Russian constitution. On the same day, Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev and his cabinet resigned and were quickly replaced. The new Prime Minister, Mikhail Mishustin, was a relatively unknown figure in Russia until recently, having previously spearheaded digital modernization efforts as head of the Federal Tax Service. The surprise changes are seen as preparation for the Putin’s departure from the presidency in 2024 given current constitutional restrictions, which prevent him from being president more than two consecutive terms. The proposed constitutional reforms would not facilitate his return to the post in the future, however, but instead propose to weaken the presidency …

From Zimbabwe to Bolivia: what makes a military coup?
Evo Morales, president of Bolivia since 2006, resigned on November 10 following weeks of demonstrations triggered by a disputed election in October. Morales won the election amid allegations that the result was rigged in his favour. The turning point in Morales’s departure from office was the intervention of Williams Kaliman, commander of the Bolivian armed forces. Speaking at a press conference, Kaliman urged Morales to resign “for the good of our Bolivia”. Morales has since gone into exile in Mexico and the manner of his departure has sparked passionate debate about whether it was tantamount to a military coup. Two years ago this month, the Zimbabwean military placed former President Robert Mugabe under house arrest. Subsequently, SB Moyo, a major …

Why Venezuela is Collapsing but President Maduro Still Standing
Creating external crises to deviate from internal problems is a well-known recipe in politics. Unpopular dictators often resort to this tactic to shape the discourse and concerns of the opposition, media, and population. In Venezuela, President Nicolas Maduro has adopted this tactic since day one. The regime’s latest attempt to induce a crisis was fabricating the notion that the opposition, in collaboration with the U.S., sought to end Maduro’s life with a drone attack. Nobody has taken this story seriously. Thus, this piece will not waste time discussing the drone affair but will instead focus on five issues that really matter. Nobody Chose This When thinking about the Venezuelan crisis, one might erroneously believe that people chose this type of …

From Scoring Goals to Winning Votes: How Three Footballers Strike Out as Politicians
George Weah’s recent election as President of Liberia is not only noteworthy for being the first peaceful transition of power in the country since 1944. His victory is also “a lesson in how sports fame can help propel figures with humble beginnings to positions of great importance.” Weah is not the only former striker who has transitioned from scoring goals to winning votes. While there is no shortage of lists of former players-turned-politicians, a closer look at three of the game’s most popular players reveals how they have leveraged their fame, wealth and appeal to mount successful populist campaigns. George Weah: President of Liberia Playing for Paris St Germain, AC Milan, Chelsea and Manchester City, George Weah is the first …

Contested Constitutions: A Microcosm of post-Arab Spring Divisions
Five years after Mohamed Bouazizi’s self-immolation in Sidi Bouzid, Tunisia ignited the Arab Spring. Yet while it inspired hope for democratic transition across the Middle East and North Africa, the region continues to be embroiled in civil war, terrorist networks, and crises of political legitimacy. In Syria and Bahrain, dictators used violence to thwart protests, leading to a prolonged civil war in Syria. In Yemen, despite the dictator’s negotiated transfer of power, rival sectarians are vying for power. In Tunisia and Egypt, dictators stepped down without much bloodshed. Lastly, in Libya, rebels overthrew the dictator with foreign military aid, but soon succumbed to factional warfare. This article will explore the interlude of democratic or semi-democratic politics in Tunisia, Egypt and …

The Democracy Commission: practically teaching democracy
The institutions, technologies and practices of British democracy are, for the most part, inventions from before the time of universal suffrage. In the fluidity and fracture of the 21st century, it is clear this democratic inheritance has become increasingly inadequate. Sharp, sustained differences in participation and voice by age, class, ethnicity and region have become entrenched. Politics has professionalised, class identities have weakened, and political parties have drifted from their anchors in civil society, left ‘ruling the void’. Reinforcing the post-democratic drift, the evolution of the UK’s political economy has shrunk the potential scope for and influence of collective political action and democratic participation. The general election clarified our evolution towards a divided democracy. As IPPR’s new report into political inequality shows, less …
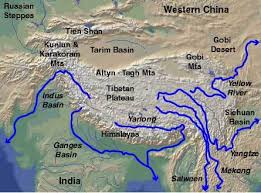
Is Water a New Flashpoint for Asia’s Rising Giants?
In the past, India and China have disputed numerous issues, from trade to territory. Notably, in 1962, disputes over their Himalayan border regions sparked the brief Sino-Indian War. In the 21st century, a new issue has the potential to become a flashpoint between the world’s most populous nations: their shared rivers.
China has planned, and in some cases begun construction on, major hydropower and water diversion projects in its southern regions, including Tibet, which is making the water security of its downstream neighbors more fragile. The glacial Tibetan Plateau, largely controlled by China, is the source of rivers that supply water to approximately 1.5 billion people. Many of Asia’s major rivers—including the Mekong, Brahmaputra, Yangtze, Yellow, Indus, and Salween Rivers—begin in the Tibetan Plateau, and supply water to people living in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Afghanistan, Nepal, and mainland Southeast Asia. Thus, China exerts powerful hegemony over Asia’s water resources.
China views the development of rivers originating within its borders as a matter of national sovereignty, not international cooperation. According to one telling Chinese proverb, “Upstream doesn’t suffer.” China does not have river treaties with other nations, making downstream countries vulnerable to water supply disruptions and other environmental damages. In the absence of treaties, downstream nations have no forums for formally resolving water disputes with China, and cannot use international legal institutions to ensure they receive their fair share of water.

A testing and tormenting time for political parties after the 2015 British general election
The ‘sweetest victory’ of the Conservatives, as David Cameron put it on May 8th, and the sweeping landslide victory of the SNP, winning all but three of the Scottish seats, were indeed shocking wake-up calls for all those concerned about British politics. Labour’s unexpectedly disastrous loss of 26 seats led Ed Miliband to announce his immediate resignation as Labour leader. The Lib-Dems were wiped away, going from 57 to just eight seats, causing the resignation of Nick Clegg as party leader. The party was severely punished by voters who blamed it for betraying everything it had stood for in seeking power. Looking at these results, one could argue that the British voters decided at the very last moment to prevent the formation of another coalition government, assumingly returning to their traditional attitude of regarding coalitions as an exception.
For the polling companies too, the election results proved a nightmare. In order to recover their privileged capacity to influence the media, voters, and parties, they are in the course of reexamining why their pre-election forecasts appeared to be inaccurate.
Meanwhile, one shall have a thorough look at how many votes the grassroots parties such as the SNP, UKIP, and the Greens, gained in this election. Even though their positions in the political spectrum span from the left to the extreme right, the total number of votes won by these three parties amounted to nearly 6.5 million, against the Conservatives’ 11.3 million. Amongst them, UKIP failed to get more than one seat and is now in the midst of an internal turmoil. Despite that, Nigel Farage is generally praised for contributing to the party’s net gain from 9.6 to 12.6 per cent of the vote. In particular, UKIP has remained popular among those who are disillusioned with the aloofness of the political elite.









